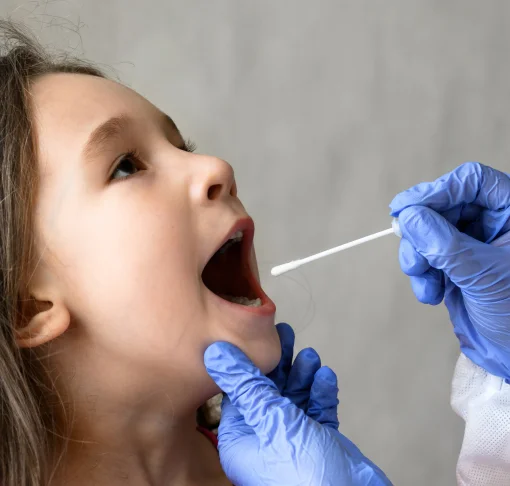
- Drug and Alcohol
Court approved hair, nail, blood drug and alcohol testing - Maternity and Paternity
Ministry of Justice approved legal DNA testing - Wider Relationships
Understanding second and third degree familial connections - Immigration
Home Office approved testing for visas and passports - Expert Services
Court standard expert witness reporting - International DNA Collection
Home Office approved DNA collection from overseas
Introduction to MDA
MDA (3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine) is a stimulant and empathogenic drug that is chemically similar to MDMA (ecstasy), but it has slightly different effects. Often referred to as the “love drug,” MDA is known for its stimulating, euphoric, and hallucinogenic properties. It has been used recreationally in social settings such as parties, raves, and music festivals. Although not as widely known as MDMA, MDA is still used illegally and is often found in “ecstasy” pills or mixed with other substances.
MDA Street Names
- MDA
- Love Drug
- Ecstasy (when mixed with MDMA)
- The “Original Ecstasy”
- Sally
- 5-Alpha
- Moonflower
MDA's Chemical Structure
MDA (3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine) shares a similar chemical structure with MDMA, featuring a methylenedioxy group attached to an amphetamine backbone. This structure allows MDA to have both stimulant and hallucinogenic effects, producing feelings of euphoria, emotional warmth, and heightened sensory perception. Its molecular formula is C10H13NO2, and like MDMA, it affects serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine levels in the brain.

How To Test For MDA
Here are the most common tests used to detect MDA and the timeframes they cover:
01
Hair
Long Detection Window (Months)

Hair tests can detect MDA for several months after use, providing a long-term record of drug use. This is often used in forensic investigations or long-term monitoring.
Explore Hair Drug Test02
Fingernail
Long Detection Window (Months)

Like hair testing, fingernail tests provide a long detection window, typically for up to several months after consumption, making it suitable for detecting MDA in individuals with a history of use.
Explore Fingernail Drug Test03
Urine
Medium Detection Window (Days)

Urine tests are commonly used to detect MDA use, typically within 1 to 3 days after consumption. However, in the case of heavy or frequent use, MDA can be detectable for a longer period.
Explore Urine Drug Test04
Blood
Short Detection Window (Hours to Days)
Blood tests are highly accurate and can detect MDA for 1 to 2 days after use. These tests are often used in emergency medical settings or legal investigations.
Explore Blood Drug Test05
Saliva
Short Detection Window (Hours to Days)

Saliva tests are useful for detecting MDA within a short window, typically up to 24 hours after use. They are often used in roadside testing or quick screenings.
Explore Saliva Drug TestLegitimate Use Cases for MDA
MDA has no current legal medical use in most countries, and its use is illegal in most places. Historically, MDA was researched for its potential use in psychotherapy, as it induces feelings of emotional closeness and increases sensory perception, similar to MDMA. However, it was never approved for medical use. MDA has been studied in clinical trials, primarily for its potential as a therapeutic adjunct in addressing emotional and psychological conditions, but these trials have been limited.
Will MDA Show Up on a Drug Test?
Yes, MDA will show up on a drug test. Drug tests that target common illicit substances, such as MDMA,amphetamine, and similar compounds, can detect MDA. It may be identified in standard drug tests used for family law, employment, law enforcement, and medical screenings, depending on the test type and the detection window.
Get a Quote
How Long Does MDA Stay in Your System?
The duration that MDA stays in your system depends on several factors, including the dose, frequency of use, metabolism, and body composition. Below are general detection windows:
- Urine Test: Detectable for 1 to 3 days
- Blood Test: Detectable for 1 to 2 days
- Hair Test: Detectable for several months
- Saliva Test: Detectable for up to 24 hours
- Nail Test: Detectable for several months
Frequent use of MDA can lead to longer detection windows as the drug builds up in the body.
Get a Quote
Factors Influencing MDA’s Presence in Your Body
Several factors can affect how long MDA stays in your system, including:
- Frequency of Use: Regular or chronic use can lead to a buildup of metabolites in the body, extending the detection window.
- Metabolism: Individuals with faster metabolisms may eliminate MDA more quickly than those with slower metabolisms.
- Hydration: Adequate hydration can speed up the excretion of MDA from the body, while dehydration can slow down the process.
- Body Fat: As a fat-soluble drug, MDA may stay in the system longer in individuals with higher body fat.
- Dosage: Higher doses of MDA may result in a longer detection window as the body processes and eliminates the substance.
MDA Use in Legal Scenarios
MDA is illegal in many countries, and a positive drug test for MDA can result in legal consequences, including fines, loss of employment, or criminal charges. MDA use can be detected in legal cases,particularly in the family law, negligence, and child custody cases,, driving under the influence, and probation monitoring. Forensic experts often test for MDA in criminal investigations and post-mortem examinations.
False Positives and Interpretation of MDA Results
False positives for MDA are rare, but they can occur. Certain medications, such as cold medications containing pseudoephedrine or some antidepressants, may cause a false positive for MDA on drug tests, at the early screening stage. More specific confirmatory tests, such as Gas Chromatography and liquid chromatography withMass Spectrometry, are often used to verify the initial results and ensure accurate detection.

Popular Culture and MDA
MDA has had a presence in popular culture, particularly within the rave and clubbing scenes. The drug is sometimes referred to as the "original ecstasy," as it was used before MDMA became widely known. It has been associated with feelings of intense euphoria, emotional warmth, and sensory enhancement. However, MDA's hallucinogenic properties can make it a more unpredictable and risky substance compared to MDMA, leading to potential negative psychological effects.
Get a Quote

Notable Forensic Cases Involving MDA
MDA has been involved in various forensic cases, particularly in drug overdose deaths and legal investigations. In post-mortem toxicology screenings, MDA may be identified as a contributing factor in fatalities, often when it has been consumed in combination with other substances. Forensic toxicologists and law enforcement agencies use specialised tests to detect MDA in samples collected during criminal investigations and accidents.
Risk of Contamination
MDA is a psychotropic substance linked to MDMA, often referred to as ecstasy. Hair analysis can identify MDA in drug testing, but there's a risk of contamination. External contamination happens when drug particles from the surroundings like smoke or physical contact accumulate on the hair, which can result in false positives. Washing procedures are employed prior to analysis to distinguish between true ingestion and contamination. Nonetheless, research indicates that certain substances, such as MDA, may attach to hair via sweat and sebum, complicating the analysis.
Get a Quote